Multivitamins are the most used supplement in every age group, according to the most recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention1 (CDC). Some people aren’t surprised by this because they know how beneficial multivitamins can be, while others might be wondering, “Do multivitamins actually work?”
Our best multivitamins for men roundup is for both types of people. We’ll provide suggestions for those who know why multivitamins can (that’s the keyword) be beneficial to our health, and for the skeptics, we’ll explain why multivitamins can be so great if you know what to look for.
Editor’s note: We intend the term “men” to include all men, including trans men. However, we recognize that almost all research on this topic has focused on cis men. For that reason, when we reference gender-based research and nutritional recommendations, we will clarify by saying “cis men.” We encourage trans and nonbinary people of all genders to check in with a trans-competent nutritionist regarding their supplements and training needs.
Why Trust Us
The GGR expert product tester team consists of certified nutrition coaches, registered dietitians, and certified personal trainers who are always searching for the highest-quality supplements, including creatine, top-rated protein powders, and greens powders. We have decades of experience in the fitness and nutrition industry, and in 2024, we helped over 1,000 consumers find the right multivitamin to support their health and wellness goals.
After researching and testing more than 20 men’s multivitamins, we followed our supplement testing methodology to rank our top picks on factors such as:
- Ingredients and dosages: Does it have a wide variety of micronutrients in research-backed doses?
- Allergens: Is it safe for everyone?
- Serving size: Are we taking one pill or four?
- Price: What is the cost per serving? Are there subscription savings?
Medical disclaimer: This article is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for medical advice. For health advice, contact a licensed healthcare provider.
13 Best Multivitamins for Men
- Best Overall Multivitamin for Men: Legion Triumph for Men
- Best Natural Multivitamin for Men: Transparent Labs Multivitamin
- Best Multivitamin for Men Over 50: Ritual Essential for Men 50+
- Best Multivitamin for Men with Iron: Ora Organic Modern Multi
- Best Multivitamin for Athletes: Momentous Essential Multivitamin
- Best Multivitamin for Men for Bodybuilding: Performix SST Multi+
- Best Multivitamin for Active Men: Onnit Total Human
- Best Vegan Multivitamin for Men: Nutricost Multivitamin
- Best Multivitamin Gummies for Men: SmartyPants Vitamins Men’s Formula
- Best Daily Multivitamin for Men: Ritual Essential for Men Multivitamin 18+
- Best Multivitamin for Men in Their 30s: MegaFood Men’s One Daily Multivitamin
- Best Multivitamin for Men Over 40: Performance Lab NutriGenesis Multi for Men
- Best Budget Multivitamin for Men: Nature Made Multivitamin for Him
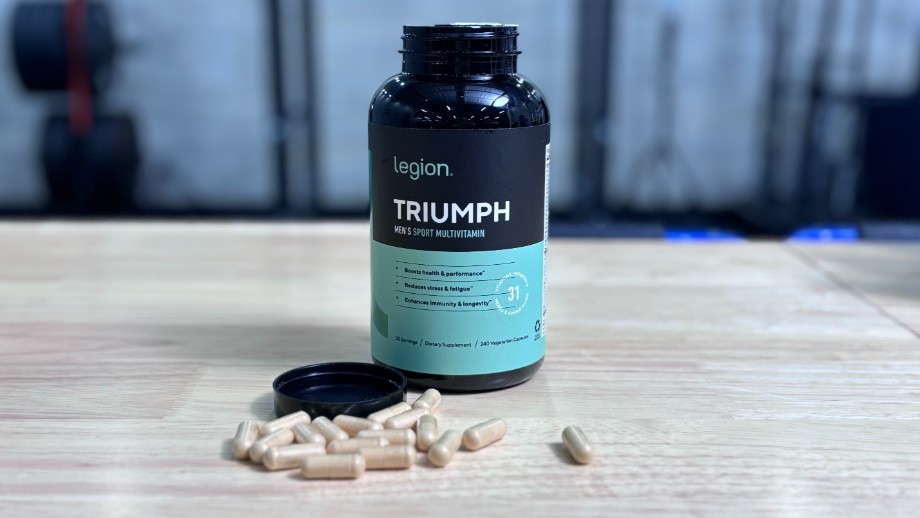
Best Overall Multivitamin for Men: Legion Triumph for Men
Good for: Those looking for a multivitamin that takes care of their mental and physical health
Legion Triumph is a multivitamin made with 100% natural ingredients and formulated with clinically effective doses of essential vitamins and minerals, as well as 10 well-researched ingredients documented to improve overall physical and mental health, athletic performance, and mood.
What our tester says:
“I noticed some slight energy improvement the following morning after taking them with dinner. But I’ll add that an eight-pill serving size is a bit ridiculous.”
Best Natural Multivitamin for Men: Transparent Labs Multivitamin
Good for: Those looking for a multivitamin without unnecessary ingredients
Transparent Labs Multivitamin is designed to support overall wellness for active adults. This supplement has limited but very positive reviews and may be sold out when you go to buy it.
What our tester says:
“It’s a bit much to take all four capsules at once since they’re rather large, and I still felt like one was stuck in my throat for a few minutes afterward.”
Best Multivitamin for Men Over 50: Ritual Essential for Men Multivitamin 50+
Good for: Men aged 50 years or older
Ritual Essential for Men Multivitamin 50+ is a supplement that is easy on the stomach and made with traceable ingredients for men 50 years old or older.
What our tester says:
“There’s an essence of mint in the flavor that could prove to e a bit too overpowering, especially if you take these first thing in the morning.”
Best Multivitamin for Men with Iron: Ora Organic Modern Multi
Good for: People who want a multivitamin with some iron
Ora Organic Modern Multi is a multivitamin that provides 20 essential nutrients that are purported to help with eye and brain health. Although the vitamins and minerals are mostly underdosed, Ora Organic claims these are the proper values needed in addition to a typical diet. The multivitamin provides these vitamins and minerals in bioavailable forms, allowing them to be absorbed better.
What our tester says:
“The capsules are about as long as the width of a quarter, so I wouldn’t imagine too many people having trouble swallowing both capsules needed for a serving.”
Best Multivitamin for Athletes: Momentous Essential Multivitamin
Good for: Athletes wanting a nutrient-dense multivitamin that’s third-party tested
Momentous Essential Multivitamin offers a blend of vitamins and minerals in healthy doses to help support energy production, immune function, antioxidant defense, and overall health. The Momentous recommends taking this multivitamin twice per day: two capsules in the morning and two capsules at night, both with food.
What our tester says:
“The serving size of four capsules is a bit much, but at least Momentous recommends breaking it up into two two-capsule servings each day.”
Best Multivitamin for Men for Bodybuilding: Performix SST Multi+
Good for: Those looking for an energy boost in the gym, along with vitamins and minerals
Performix SST Multi+ is a multivitamin aimed to fuel high-performing lifestyles with a blend of vitamins, minerals, caffeine, and grains of paradise (which offers potential fat-burning capabilities). SST Multi+ has 80 mg of caffeine, which is less than the average cup of coffee brewed at home (around 90 to 120 mg of caffeine).
What our tester says:
“This was nice to help boost my energy, but it may not be the best multivitamin if you have any serious iron deficiency.”
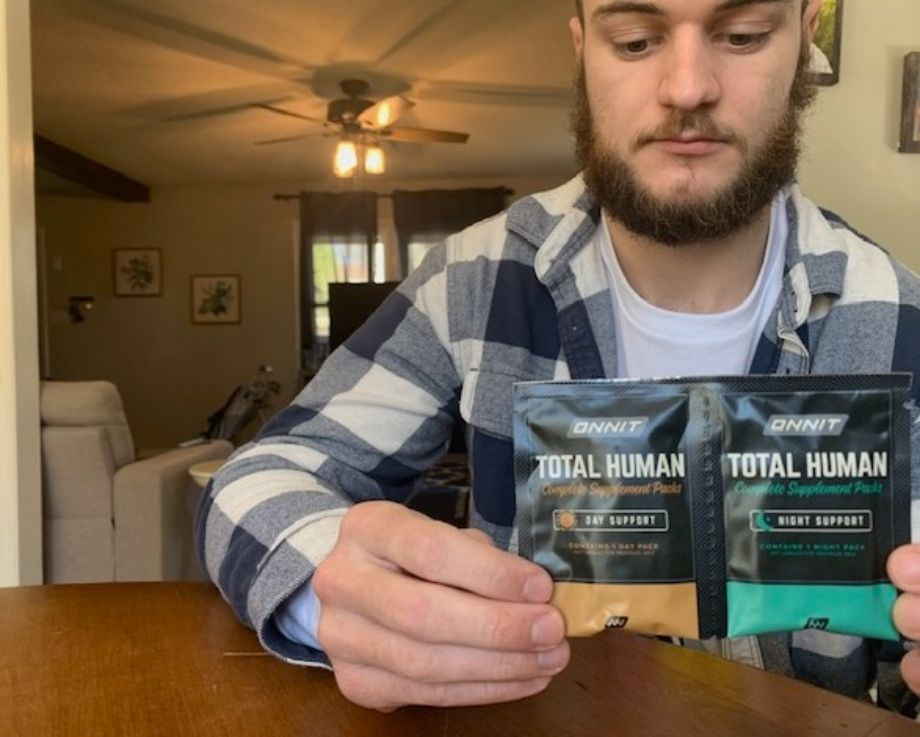
Best Multivitamin for Active Men: Onnit Total Human
Good for: Anyone looking for a multivitamin package to compliment an active lifestyle
Onnit Total Human is an expensive supplement pack with a lot of pills, designed for people that want everything they need in one place and want to use a variety of Onnit’s products.
What our tester says:
“I feel a lot clearer with noticeably less brain fog. I truly feel very good when I take these, and if I miss a day, I notice the difference.”
Best Vegan Multivitamin for Men: Nutricost Multivitamin
Good for: Those who want to fill nutritional gaps and look after their gut health
Nutricost Multivitamins has research-backed doses of 22 vitamins and minerals, and is also one of the most affordable multivitamin supplements.
What our tester says:
“If you find yourself struggling to get enough micronutrients through diet alone, this multivitamin is likely to cover any nutrient gaps you may have.”
Best Multivitamin Gummies for Men: SmartyPants Vitamins Men’s Formula
Good for: Anyone who prefers to take their supplements in gummy form
SmartyPants Vitamins Men’s Formula gummies have good reviews, but you’ll have to take a lot of gummies to see the benefit.
What our tester says:
“One gummy is about the size of a dime. It had the texture of an orange slice, but isn’t as chewy as a gummy bear.”
Best Daily Multivitamin for Men: Ritual Essential for Men Multivitamin 18+
Good for: Folks who want a simple but effective daily multivitamin
The Ritual Essential for Men Multivitamin 18+ is a well reviewed multivitamin with quality ingredients. The only notable complaint was the mint flavoring.
What our tester says:
“I like the minty essence, but I could see it being a bit overpowering on an empty stomach.”
Best Multivitamin for Men In 30s: MegaFood Men’s One Daily Multivitamin
Good for: Folks who take a multivitamin first thing in the morning or who want to avoid upset stomachs
The MegaFood Men’s One Day Multivitamin is a customer-approved option with the ability to purchase in 30-,60-, and 90-day supplies.
What our tester says:
“I hardly noticed any flavor when I took this daily multivitamin, which makes it easier to swallow, although the texture was a bit chalky.”
Best Multivitamin for Men Over 40: Performance Lab NutriGenesis Multi for Men
Good for: Anyone who prefers to put their supplements on a subscription basis
NutriGenesis Multi for Men is a plant-based vitamin that contains 26 vitamins and minerals and no fillers or additives. Performance Lab claims their multivitamin helps support energy metabolism, gut health, healthy aging, muscle, bone and joint health, immune function and masculine vitality. There are mixed customer reviews with some customers reporting that they did not feel a difference and others feeling they feel healthier with more energy.
What our tester says:
“I haven’t really prioritized my micronutrients as well as I should recently, so this has helped give me a slight edge and boost, from what I’ve felt over the last several days.”
Best Budget Multivitamin for Men: Nature Made Multivitamin for Him
Good for: Those on a budget
Despite some complaints of stomach discomfort, Nature Made Multivitamin for Him is an affordable multivitamin option that may be a good choice for you.
What our tester says:
“The taste of the tablet was sort of like wheat grass, like many multivitamins can taste like. It’s not the worst flavor or bitter at all, but it’s also not something that I would like to savor for the rest of my morning.”
Other Men’s Multivitamins We Researched
Here are some other notable multivitamins we tested and researched:
- AG1 Next Gen: While this isn’t “technically” a multivitamin, Athletic Greens is a rich source of vitamins and minerals in addition to adaptogens, probiotics, and whole food-sourced ingredients that are beneficial to our overall health. Unsure if Athletic Greens is for you? Read our full Athletic Greens review.
- 1st Phorm Micro Factor: This is similar to Onnit Total Human in that it’s six supplements in one: a multivitamin, antioxidants, a probiotic, CoQ10, Essential Fatty Acids, and Fruits and Vegetables. Consider this the budget-friendly version of Onnit, with the trade-off being that you get fewer supplements and lower dosages. It’s still a great product, but if you have the money for Onnit, we’d recommend it over 1st Phorm.
- Rootine Smart Multivitamins: These unique multivitamins use DNA testing to determine proper doses of vitamins and minerals for you. We like the personal touch of this multivitamin, but with that personalization comes a pricey cost of about $90 for a month’s supply. Read more in our Rootine Vitamins review.
How We Picked and Tested the Best Multivitamins for Men
We’ll explain briefly why it’s so hard to pick a multivitamin that works for everyone, but there are some things that separate a good multivitamin from a bad one.
- Expert recommendations: All of the multivitamins on this list were reviewed and green-lighted by our experts to ensure that we only recommended high-quality, effectively dosed products.
- Nutrients and dosages: We wanted to find multivitamins that included moderate to high amounts of vitamins and minerals, though for things like iron and selenium, they should be present in lower amounts to avoid dangerous side effects.
- Variety: We looked for multivitamins that had a good variety of key nutrients.
- Price: We wanted to make sure each supplement was generally affordable for most people.
- Taste and swallowability: What form does it come in and how easy was it to take the multivitamin?
- Quality testing: The best multivitamin brand for men should be transparent and contain high-quality ingredients. We looked for multivitamins that had some kind of third-party testing to ensure each was free from banned substances and had an accurate label. If a product was not third-party tested, we evaluated whether the label was transparent and the company seemed trustworthy. All of the multivitamins on this list checked one of these two boxes.
What Vitamins and Minerals Do Men Need?
Men’s and women’s bodies are different in many ways, so it makes sense that men require different vitamins and minerals than women. Men should look for a multivitamin supplement that’s tailor-made for their needs. Here are the vitamins and minerals men should look for in a multivitamin.
- Vitamin A: Vitamin A supplementation can help slow age-related vision loss20. According to research evidence37, it may also help improve reproductive and cellular health and reduce the risk of some cancers.
- B Vitamins: B Vitamins have been linked with improved cellular health, immune function, and cognition22, and it may also help slow the aging process30.
- Vitamin C: There’s much more to vitamin C than its immune-boosting properties. For example, it could help your body better absorb other nutrients such as iron38 and according to researchers39 could help alleviate early symptoms of osteoarthritis.
- Vitamin D: Your body needs vitamin D to fully absorb calcium and phosphorus, making it a vital nutrient for those looking after their bone health8. Harvard Medical School40 states it may help reduce cancer cell growth, reduce inflammation, and aid the body in fighting infections.
- Vitamin E: Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant to protect your cells’ membranes to support blood, brain, and skin health, according to researchers41.
- Vitamin K: Adult cis men need vitamin K to help with blood, heart, and bone health42.
- Thiamin: Thiamin, sometimes called thiamine or vitamin B1, “plays a critical role in energy metabolism and, therefore, in the growth, development, and function of cells,” according to the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Dietary Supplements43.
- Riboflavin: Riboflavin, sometimes referred to as vitamin B2, plays a vital role in helping the body properly convert food into energy and may help you better utilize certain prescription drugs, according to the NIH44.
- Biotin: Most cis men don’t struggle with getting enough biotin, sometimes called vitamin H or vitamin B7, as it is prevalent in many food sources. Those who don’t get enough of it may experience thinning hair, cracked skin, loss of appetite, or fatigue, according to Mount Sinai45.
- Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 is often found in animal-based products, so vegetarians or vegans will definitely want a multivitamin with this nutrient. It’s responsible for red blood cell formation and DNA synthesis10.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3s are beneficial for heart and joint health2.
- Boron: Studies have shown that boron can help improve the brain’s electrical activity8.
- Iron: Iron deficiency is the most common nutritional deficiency. It can cause anemia13, which may lead to fatigue, hair loss, and poor temperature regulation19.
- Zinc: Zinc supplementation could help improve men’s overall testosterone levels16 and may have anti-aging properties18.
- Calcium: Calcium is essential for bone health and muscle contractions and is used in cardiac function46.
- Selenium: Selenium is vital to overall cellular health27.
- Magnesium: Sometimes called the “forgotten electrolyte47,” magnesium is involved in over 300 cellular processes in the body.
Ingredients To Pay Attention To (and Avoid)
While multivitamins can be a great addition to those dealing with vitamin or mineral deficiencies, not every multivitamin is built the same. Some may have fillers that should be avoided in large quantities. Ideally, your multivitamin should contain the micronutrients you need and little else.
Make sure to talk to your physician or a licensed professional to help weight the risks and benefits of supplements. That said, here are some common ingredients to be aware of (and in some cases avoid altogether):
Additives and Fillers
Fillers do just as their name suggests: They fill and add substance to a vitamin tablet or capsule. Additives can be used in multivitamins to increase their shelf life, bind ingredients, or to improve the flavor and texture of vitamins. Common additives used in supplements are:
- Cellulose
- Gelatin
- Soy Lecithin
- Magnesium stearate
- Maltodextrin
- Soybean oil
- Citric acid
- Sorbitol
While additives and fillers may be necessary in some products, a best practice is to avoid supplements and multivitamins with a large amount of additives and fillers.
Dyes and Coloring
Food and supplements can often contain food dyes to create a more appetizing hue for consumers. However, some studies and reviews48 show several food dyes to be carcinogenic or contaminated with other common carcinogens. Others caused hypersensitivity reactions. While more research needs to be done on these dyes, avoid multivitamins with these dyes.
Artificial Sweeteners
Some chewable vitamins may have added sugars, artificial sweeteners, or sugar alcohols. Sugar alcohols can cause digestive distress in some people (especially in larger quantities). Artificial and non-caloric sweeteners have been associated with cardiovascular disease in some observational studies, according to a 2024 review49. Exercise caution when choosing a supplement with artificial sweeteners.
Safety and Precautions
Even though multivitamins can be beneficial, there are some risks to taking supplements. If you have allergies, check your new multivitamins for any allergens, such as soy or tree nuts. Also, consult with a doctor or specialist before adding a new supplement to your regimen.
Some multivitamins may also contain gluten, so individuals who are sensitive to gluten should check labels carefully to find certified gluten-free versions.
Dr. Jennie Stanford
Benefits of Multivitamins
Before we start listing all the benefits of a multivitamin, we must remind you that you should get all your vitamins and minerals from whole foods (not the grocery store chain, but actual foods like meat, dairy, vegetables, fruits, and cheese). Depending on what you eat, how much of it you consume, and any medical conditions you have, you may still have different nutritional needs to address. For example, a plant-based eater will often be lower in iron than someone who eats red meat.
That said, we think there are a few main benefits of taking a multivitamin:
Convenience
A multivitamin allows you to fill those nutritional gaps in a much more affordable, convenient, and healthful way than eating extra food to obtain the micronutrients you might be lacking.
RELATED: Best Whey Protein
Maintains Bodily Functions
Our body requires micronutrients for vision, immune health, physical activity, focusing…you get it, they’re essential to everyday life. Without them, we can start to feel sluggish or even experience health problems. A multivitamin allows you to maintain optimal health by ensuring you’re getting all essential nutrients.
RELATED: Best Pre-Workout for Women
Addresses Unique Nutritional Needs and Health Concerns
Someone who’s not getting a lot of vitamin D from their diet will need a different multivitamin than someone who has adequate vitamin D but is deficient in vitamin A. Furthermore, according to Dr. Raj Dasgupta, MD, FACP, FCCP, FAASM, “Vegans can benefit from multivitamin supplementation to ensure they get essential nutrients that may be missed from following a plant-based diet, such as vitamin B12, vitamin D, calcium, iron, omega-3 fatty acids, and iodine.”
Some micronutrients can be harmful if ingested in excessive amounts, like iron and selenium. Taking a multivitamin with those two minerals can actually be dangerous to someone who’s already getting enough of them through their diet, even though they still may be deficient in other vitamins and minerals.
That’s all to say, please contact your physician or nutritionist before starting a multivitamin. They’ll be the best person to tell you which one is right for you.
How to Choose a Multivitamin for Men
This is a very difficult question because it truly depends on you and your health, diet, and overall health goals. Here are several things to consider when choosing a multivitamin for men:
- Age: “Because of age-related changes in nutrient absorption and metabolism, men over 50 are more prone to nutrient deficiencies. A multivitamin can help address these concerns and support men’s overall health, including bone strength, heart health, and cognitive function,” says Dr. Raj Dasgupta, MD, FACP, FCCP, FAASM.
- Lifestyle: Choose a multivitamin with the nutrients that can support your lifestyle.
- Dietary restrictions: Make sure the men’s multivitamin doesn’t contain any allergens or ingredients that might go against your faith (many of our top picks are Kosher and Halal).
- Allergies: Some vitamins and ingredients present in a multivitamin—like coloring agents, herbs, spices, and even the vitamins themselves—can cause an allergic reaction in some people. If you know you’re allergic to something, do your due diligence to check the label before taking a multivitamin.
- Budget: Multivitamins can range in price from $0.15 per serving to $3 per serving for a customized option. If this is something you’ll take daily, figure out how much you’re willing to spend. A budget-friendly option isn’t inherently less effective than a more expensive option, so shop around and do your research.
- Form: Many multivitamins come in capsules, tablets, or soft gels, but you can also find them in gummy, chewable, powder, or liquid forms. Each form has benefits and drawbacks. For instance, although gummies taste great, they may be inaccurately labeled50 more frequently and can lose potency over time51. Capsules are generally flavorless and the easiest to swallow but generally contain fewer ingredients than tablets. You may need to take more capsules than you would with tablets. It’s best to talk with your doctor about what your best option is.
RELATED: Best Protein Shakes
Who Should Take Men’s Multivitamins?
Whether or not you need to take a men’s multivitamin typically depends on your age and whether you’re regularly consuming a diet rich in essential nutrients. Unfortunately, Americans are notorious for under-consuming important nutrients and minerals, with the top four being vitamin D, dietary fiber, calcium, and potassium52. If you can reach your recommended daily intake of these nutrients from your diet alone, great! If not, vitamins for men can come in clutch.
Similarly, older adults are more at risk for vitamin deficiencies and may need supplemental help from a multivitamin. If you’re unsure if a daily multivitamin suits your current dietary needs, consult with your primary care physician or a registered dietitian to assess whether you may have certain vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
Who Should Avoid Men’s Multivitamins?
Multivitamins are generally harmless, especially if you’re taking one that has been third-party tested and contains reasonable amounts of each nutrient—meaning nothing above the daily intake. If anything, they’re considered unnecessary if you’re reaching your dietary needs through a healthy, well-balanced diet.
That said, if you’re a current or past smoker, you’ll want to avoid a multivitamin that is too high in beta carotene (vitamin A), as more than 20 milligrams (7,500 mcg) per day may put you at higher risk of lung cancer53. However, current evidence is inconclusive.
Experts Who Contributed to This Article
FAQs About Best Multivitamins for Men
What is the top-rated men’s multivitamin?
Some of the top-rated multivitamins for men that were also favorites amongst our testers and nutrition experts are Ritual Essential for Men Multivitamin 18+, Transparent Labs Multivitamin, and Legion Triumph for Men.
Do men’s multivitamins really work?
Men’s multivitamins can help fill nutrient gaps if you’re deficient in certain key vitamins and minerals. However, it’s important to speak with a physician before taking one to ensure it will address your specific needs. In some cases, taking a multivitamin can be harmful because you may end up consuming too much of a specific vitamin or mineral. Getting most of your nutrients from whole food sources is always the best place to start.
What is the best vitamin for men over 50?
We like Ritual Essential for Men 50+ for men over 50 because it contains several key vitamins and minerals that older men need for optimal health. It’s also certified carbon-free, Clean Label Project-certified, Non-GMO Project-verified, and vegan.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any diseases.
References
- Mishra, S., Stierman, B., Gahche, J. J., & Potischman, N. (2021). Dietary supplement use among adults: United States, 2017–2018.
- Ghasemi Fard, S., Wang, F., Sinclair, A. J., Elliott, G., & Turchini, G. M. (2018). How does high DHA fish oil affect health? A systematic review of evidence. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 59(11), 1684–1727. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1425978
- Stiefvatter, L., Lehnert, K., Frick, K., Montoya-Arroyo, A., Frank, J., Vetter, W., … & Bischoff, S. C. (2021). Oral bioavailability of omega-3 fatty acids and carotenoids from the microalgae Phaeodactylum tricornutum in healthy young adults. Marine drugs, 19(12), 700.
- Malík, M., & Tlustoš, P. (2022). Nootropics as Cognitive Enhancers: Types, Dosage and Side Effects of Smart Drugs. Nutrients, 14(16), 3367. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163367
- Skvarc, D. R., Dean, O. M., Byrne, L. K., Gray, L., Lane, S., Lewis, M., … & Marriott, A. (2017). The effect of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on human cognition–A systematic review. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 78, 44-56.
- Bonilla, D. A., Moreno, Y., Gho, C., Petro, J. L., Odriozola-Martínez, A., & Kreider, R. B. (2021). Effects of Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) on physical performance: Systematic review and bayesian meta-analysis. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 6(1), 20.
- Sarmiento, A., Diaz-Castro, J., Pulido-Moran, M., Kajarabille, N., Guisado, R., & J Ochoa, J. (2016). Coenzyme Q10 supplementation and exercise in healthy humans: A systematic review. Current Drug Metabolism, 17(4), 345-358.
- Pizzorno, L. (2015). Nothing boring about boron. Integrative Medicine: A Clinician’s Journal, 14(4), 35.
- Holick, M. F. (2024). Vitamin D and bone health: What vitamin D can and cannot do. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research, 109, 43-66.
- O’Leary, F., & Samman, S. (2010). Vitamin B12 in health and disease. Nutrients, 2(3), 299-316.
- Quigley, E. M. (2019). Prebiotics and probiotics in digestive health. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 17(2), 333-344.
- Latunde-Dada, G. O. (2024). Iron Intake and Human Health. Nutrients, 16(2), 206.
- Fischer, J. A. J., Cherian, A. M., Bone, J. N., & Karakochuk, C. D. (2023). The effects of oral ferrous bisglycinate supplementation on hemoglobin and ferritin concentrations in adults and children: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrition reviews, 81(8), 904–920. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuac106
- Li, N., Zhao, G., Wu, W., Zhang, M., Liu, W., Chen, Q., & Wang, X. (2020). The Efficacy and Safety of Vitamin C for Iron Supplementation in Adult Patients With Iron Deficiency Anemia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA network open, 3(11), e2023644. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.23644
- Mrowicka, M., Mrowicki, J., Kucharska, E., & Majsterek, I. (2022). Lutein and Zeaxanthin and Their Roles in Age-Related Macular Degeneration-Neurodegenerative Disease. Nutrients, 14(4), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14040827
- Prasad, A. S., Mantzoros, C. S., Beck, F. W., Hess, J. W., & Brewer, G. J. (1996). Zinc status and serum testosterone levels of healthy adults. Nutrition, 12(5), 344-348.
- Kaur, D., Rasane, P., Singh, J., Kaur, S., Kumar, V., Mahato, D. K., … & Kumar, S. (2019). Nutritional interventions for elderly and considerations for the development of geriatric foods. Current Aging Science, 12(1), 15-27.
- Cabrera, A. J. R. (2015). Zinc, aging, and immunosenescence: an overview. Pathobiology of Aging & Age-related Diseases, 5(1), 25592.
- Simes, D. C., Viegas, C. S., Araújo, N., & Marreiros, C. (2019). Vitamin K as a powerful micronutrient in aging and age-related diseases: pros and cons from clinical studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4150.
- Khoo, H. E., Ng, H. S., Yap, W. S., Goh, H. J. H., & Yim, H. S. (2019). Nutrients for prevention of macular degeneration and eye-related diseases. Antioxidants, 8(4), 85.
- Gupta, C., & Prakash, D. (2014). Phytonutrients as therapeutic agents. Journal of Complementary & Integrative Medicine, 11(3), 151–169. https://doi.org/10.1515/jcim-2013-0021
- Kennedy, D. O. (2016). B vitamins and the brain: mechanisms, dose and efficacy—a review. Nutrients, 8(2), 68.
- Murdolo, G., Bartolini, D., Tortoioli, C., Piroddi, M., Torquato, P., & Galli, F. (2017). Selenium and cancer stem cells. Advances in Cancer Research, 136, 235-257.
- Tsugawa, N., & Shiraki, M. (2020). Vitamin K nutrition and bone health. Nutrients, 12(7), 1909.
- Kim, M. G., Yang, I., Lee, H. S., Lee, J. Y., & Kim, K. (2020). Lipid-modifying effects of krill oil vs fish oil: A network meta-analysis. Nutrition Reviews, 78(9), 699-708.
- Calella, P., Cerullo, G., Di Dio, M., Liguori, F., Di Onofrio, V., Gallè, F., & Liguori, G. (2022). Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of spirulina in exercise and sport: A systematic review. Frontiers in Nutrition, 9, 1048258. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.1048258
- Todorova, V., Ivanov, K., Delattre, C., Nalbantova, V., Karcheva-Bahchevanska, D., & Ivanova, S. (2021). Plant adaptogens—History and future perspectives. Nutrients, 13(8), 2861.
- Solomon, T. M., Leech, J., deBros, G. B., Murphy, C. A., Budson, A. E., Vassey, E. A., & Solomon, P. R. (2016). A randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled, parallel group, efficacy study of alpha BRAIN® administered orally. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental, 31(2), 135-143.
- Yoneshiro, T., Matsushita, M., Sugita, J., Aita, S., Kameya, T., Sugie, H., & Saito, M. (2021). Prolonged Treatment with Grains of Paradise (Aframomum melegueta) extract recruits adaptive thermogenesis and reduces body fat in humans with low brown fat activity. Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology, 67(2), 99-104.
- Mikkelsen, K., & Apostolopoulos, V. (2018). B vitamins and ageing. Biochemistry and Cell Biology of Ageing: Part I Biomedical Science, 451-470.
- Sanders, A. E., Shaikh, S. R., & Slade, G. D. (2018). Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and headache in the US population. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids, 135, 47-53.
- Imran, M., Ghorat, F., Ul-Haq, I., Ur-Rehman, H., Aslam, F., Heydari, M., … & Rebezov, M. (2020). Lycopene as a natural antioxidant used to prevent human health disorders. Antioxidants, 9(8), 706.
- Chen, P., Zhang, W., Wang, X., Zhao, K., Negi, D. S., Zhuo, L., … & Zhang, X. (2015). Lycopene and risk of prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine, 94(33), e1260.
- Greenway, F., Fujioka, K., & Yu, Y. (2011). Vomiting from multivitamins: A potential drug interaction. American Journal of Therapeutics, 18(6), 453-457.
- Baltaci, A. K., Mogulkoc, R., & Baltaci, S. B. (2019). The role of zinc in the endocrine system.
- Scaglione, F., & Panzavolta, G. (2014). Folate, folic acid and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate are not the same thing. Xenobiotica, 44(5), 480-488.
- Carazo, A., Macáková, K., Matoušová, K., Krčmová, L. K., Protti, M., & Mladěnka, P. (2021). Vitamin A update: forms, sources, kinetics, detection, function, deficiency, therapeutic use and toxicity. Nutrients, 13(5), 1703.
- Li, N., Zhao, G., Wu, W., Zhang, M., Liu, W., Chen, Q., & Wang, X. (2020). The efficacy and safety of vitamin C for iron supplementation in adult patients with iron deficiency anemia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA network open, 3(11), e2023644-e2023644.
- Ripani, U., Manzarbeitia-Arroba, P., Guijarro-Leo, S., Urrutia-Graña, J., & De Masi-De Luca, A. (2019). Vitamin C may help to reduce the knee’s arthritic symptoms. Outcomes assessment of nutriceutical therapy. Medical Archives, 73(3), 173.
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. (2024, May 9). Vitamin D. The Nutrition Source.
- Xiong, Z., Liu, L., Jian, Z., Ma, Y., Li, H., Jin, X., … & Wang, K. (2023). Vitamin E and multiple health outcomes: an umbrella review of meta-analyses. Nutrients, 15(15), 3301.
- Hariri, E., Kassis, N., Iskandar, J. P., Schurgers, L. J., Saad, A., Abdelfattah, O., … & Kapadia, S. (2021). Vitamin K2—a neglected player in cardiovascular health: a narrative review. Open Heart, 8(2), e001715.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2023, February 9). Office of dietary supplements – thiamin. NIH Office of Dietary Supplements.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2022, May 11). Office of dietary supplements – riboflavin. NIH Office of Dietary Supplements.
- Vitamin H (biotin). Mount Sinai Health System. (n.d.).
- Drake TM, Gupta V. Calcium. [Updated 2024 Jan 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557683/
- Ahmed, F., & Mohammed, A. (2019). Magnesium: the forgotten electrolyte—a review on hypomagnesemia. Medical Sciences, 7(4), 56.
- Kobylewski, S., & Jacobson, M. F. (2012). Toxicology of food dyes. International journal of occupational and environmental health, 18(3), 220–246. https://doi.org/10.1179/1077352512Z.00000000034
- Warner J. O. (2024). Artificial food additives: hazardous to long-term health?. Archives of disease in childhood, 109(11), 882–885. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2023-326565
- Cohen, P. A., Avula, B., Wang, Y. H., Katragunta, K., & Khan, I. (2023). Quantity of melatonin and CBD in melatonin gummies sold in the US. JAMA, 329(16), 1401-1402.
- UCLA Health. Should you take gummy vitamins? Published 2022 Dec 12.
- Higgins, C. (2020, May 7). Top 10 Underconsumed Nutrients in America. Designs for Health. Accessed 10/03/2024 from:
- Hemilä, H. (2020). The effect of β-carotene on the mortality of male smokers is modified by smoking and by vitamins C and E: evidence against a uniform effect of nutrient. Journal of Nutritional Science, 9, e11.