Whether via an adjustable kettlebell set or landmine attachment to immensely diversify your home gym, uniqueness paired with functionality truly excites us. And if there’s any nutrient that marries the two, it’s vitamin D—affectionately known as the “sunshine vitamin” and truly one-of-a-kind.
Yes, you can find vitamin D in foods (like any nutrient). But it’s also sourced from sweet sunshine (unlike any other nutrient). Unfortunately, vitamin D deficiency1 is an emerging health condition worldwide and available data2 points out that 25% to 50% (or more!) of patients in clinical practice are deficient in the vitamin. This can increase the risk of broken bones, muscle weakness, and seizures, just to name a few.
We absolutely encourage a foods-first approach and the great outdoors. But if you’re needing a vitamin D boost, like most of the world, look no further than this best vitamin D supplement round-up.
As a registered dietitian (RD), I personally evaluated the products on this list (as well as others our team researched). We had members of the GGR team, including personal trainers and certified nutrition coaches, personally test each of these products. Together, we rated each supplement on the formulation, dosage, price, and side effects.
Through applying our in-depth supplement testing methodology, we arrived at the best vitamin D supplements on the market by looking at these factors:
- Formulation: Does it have at least 1,000 IU (25 micrograms) of Vitamin D3 and contain no added sugars or unstable oils?
- Swallowability: Can it be easily swallowed?
- Third-party testing: Does the company use third-party testing to ensure there are no banned/harmful substances?
- Price per serving: Products gets a 4-5 out of 5 if the price per serving is $0.10 or lower.
Medical disclaimer: This article is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for medical advice. For health advice, contact a licensed healthcare provider.
Best Vitamin D Supplements for 2026
- Best Vitamin D Supplement Overall: Transparent Labs Vitamin D3+K2
- Best High-Dose Vitamin D Supplement: Sports Research Vitamin D3
- Best Budget Vitamin D Supplement: Nutricost Vitamin D3 Softgels
- Best Vegan Vitamin D Supplement: Utzy Naturals Vitamin D3+K2
- Best Vitamin D Supplement for Men: Ritual Essential for Men 18+
- Best Chewable Vitamin D Supplement: Ora Organic Sol Food High-Potency Vitamin D3+K2
- Best Softgel Vitamin D Supplement: True Nutrition Vitamin D3
- Best Liquid Vitamin D Supplement: Athletic Greens D3+K2 Liquid
- Best Gummy Vitamin D Supplement: Bulletproof A+D+K Gummy
- Best Vitamin D and K Supplement: Thorne Vitamin D/K2 Drops
- Best Organic Vitamin D Supplement: Garden of Life Raw Whole Food Vitamin D
- Best Vitamin D Supplement for Kids: Carlson Labs Kid’s Super Daily D3 + K2
- Best Vitamin D Supplement for Black Women: Mela Vitamins Daily Essentials for Women
- Best Calcium and Vitamin D Supplement: Thorne Advanced Bone Support
- Best Vitamin D Supplement for Women: Ritual Essential for Women 18+
Let’s Quickly Chat Vitamin D
Before diving straight into our top picks, let’s get a better understanding of vitamin D. At its essence, vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin3 essential for bone, immune, heart, and mental health. (The nutrient also plays other vital health roles that we’ll dive into in the next upcoming sections, so be sure to stick around.)
Vitamin D is also very unique in that not only is it sourced naturally from foods, but also from glorious sunshine—which is why vitamin D is also known as the “sunshine vitamin.” The vitamin D we get from sun exposure is known as vitamin D3, although vitamin D2 is another form of the vitamin.
Vitamin D2 vs Vitamin D3
Vitamin D primarily exists in two forms: vitamin D2 and vitamin D3. While their structures and uses are similar, the potency of vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 appears to be different. Bear with us here—while the differences are subtle, they make a world of difference in which form might be best to supplement with.
We’ll first discuss vitamin D3, also known as cholecalciferol, for explanation purposes. Vitamin D3 naturally occurs in a select few food sources—like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified products such as cereal—but is mainly synthesized by the human body, especially when skin is exposed to sunlight.
Vitamin D2, or ergocalciferol, is also synthesized by sunlight but by plants instead of the human body. What this means is that plants—such as mushrooms and yeasts—synthesize vitamin D from the sun and humans can obtain vitamin D2 by consuming the aforementioned foods.
Interestingly, both vitamin D2 and D3 are absorbed, metabolized, and used in the body similarly, However, older research4 shows vitamin D2 is much less effective in the body and that vitamin D3 is more effective in increasing blood levels of vitamin D in the blood.
Overall, both vitamin D2 and D3 are functional forms of vitamin D and you could certainly get enough vitamin D from either. But, you would have to consume a lot more vitamin D2 to reach an adequate level—and what this really comes down to is a “work smarter, not harder” approach, and why you’ll notice all of our top picks include vitamin D3 as its primary form.
All this said, let’s explore our (sun)shining vitamin D picks!
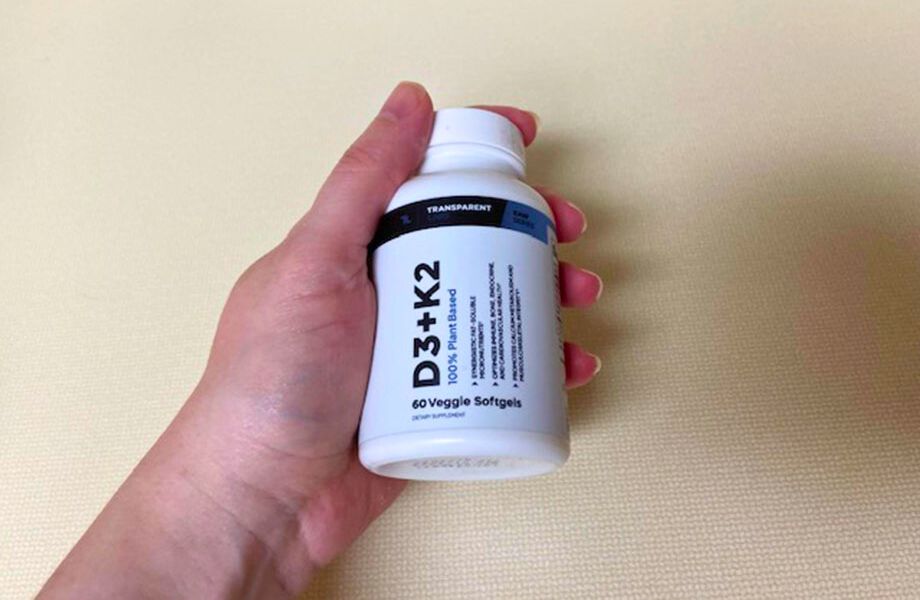
Best Vitamin D Supplement Overall: Transparent Labs Vitamin D3+K2
Good for: Anyone looking for a high-quality vitamin D supplement with added benefits of vitamin K2
Transparent Labs Vitamin D3 + K2 combines the two vitamins to maximize benefits. Each pill has 5,000 IUs of vitamin D3 and 100 mcg of vitamin K2. Customer reviews are limited but mostly positive for this product.
What our tester says:
“These pills are easy to swallow. They’re totally inoffensive, especially because they don’t give off an aftertaste or oily burps.”
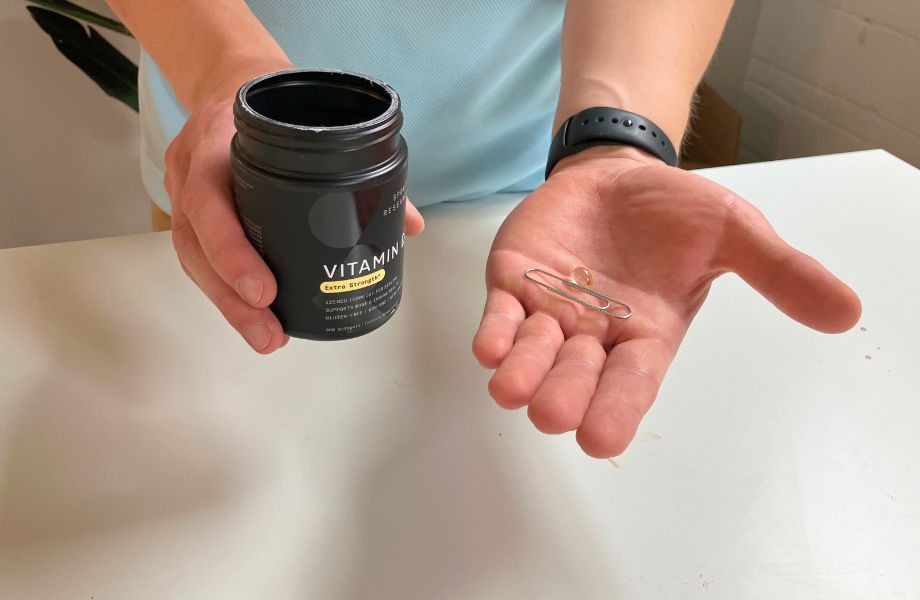
Best High-Dose Vitamin D Supplement: Sports Research Vitamin D3
Good for: Those seeking a high-quality, effective dose of vitamin D
Sports Research Vitamin D3 is only available in one dosage, 10,000 IU. Be aware if you are allergic to tree nuts, as it also contains coconut MCT oil to help with absorption. This supplement is designed to support calcium absorption, bone development, and the immune system.
What our tester says:
“With a smooth exterior and small size, these softgels are very easy to take, and I like the third-party testing so I know that what I’m taking is free from contaminants.”
Best Budget Vitamin D Supplement: Nutricost Vitamin D3 Softgels
Good for: Anyone looking for quality vitamin D on a budget
Nutricost offers an excellent price per serving value when it comes to Vitamin D3 supplementation.
What our tester says:
“I’ve definitely noticed a difference in my energy levels since starting to supplement with Nutricost.”
Best Vegan Vitamin D Supplement: Utzy Naturals Vitamin D3+K2
Good for: Plant-based eaters seeking a high-quality, effective dose of vitamin D
Utzy Naturals contains a synergistic partnership of vitamins D3 and K2 in scientifically-backed dosages. It’s manufactured in the USA in an NSF-registered facility, is tested for purity and potency, and has an “empty bottle” guarantee.
What our tester says:
“This product is third-party tested, manufactured in the United States, and comes with an empty-bottle guarantee you won’t see with a lot of other supplements.”
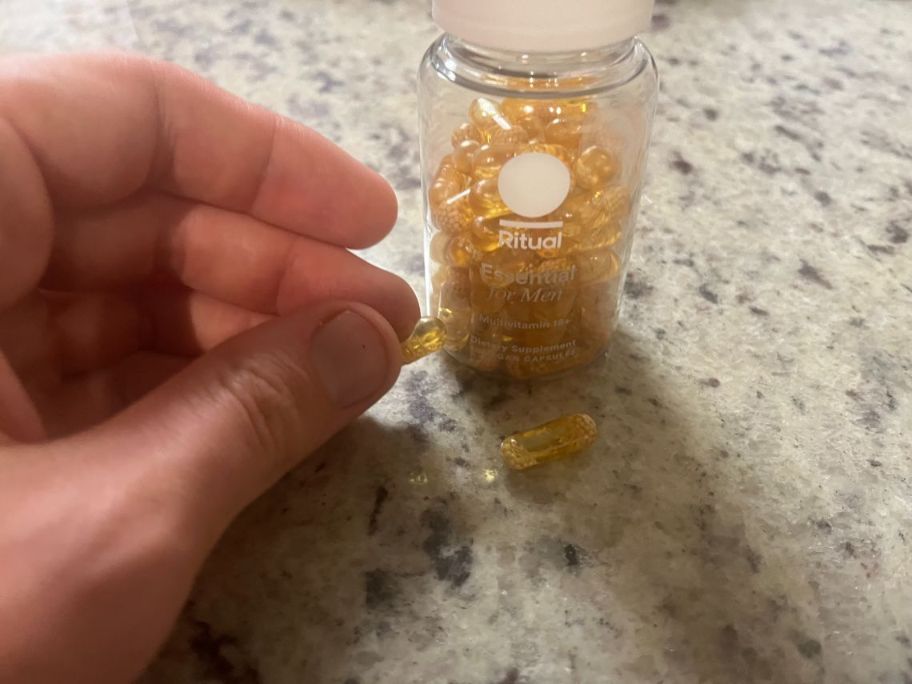
Best Vitamin D Supplement for Men: Ritual Essential for Men 18+
Good for: Men seeking a high-quality, effective dose of vitamin D
The Ritual Essential for Men Multivitamin 18+ is a well reviewed multivitamin with quality ingredients. The only notable complaint was the mint flavoring.
What our tester says:
“I like the minty essence, but I could see it being a bit overpowering on an empty stomach.”
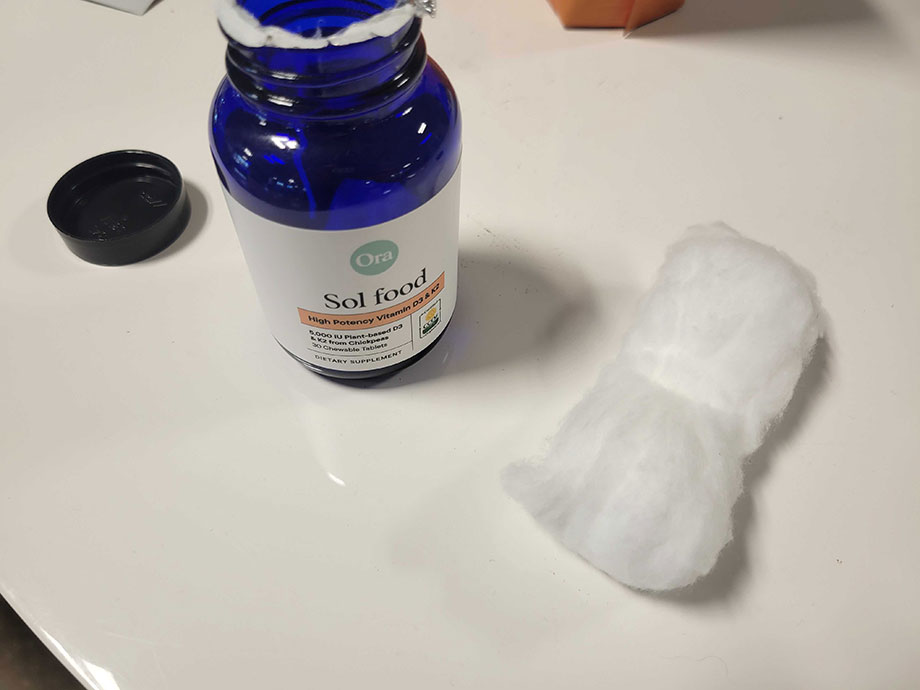
Best Chewable Vitamin D Supplement: Ora Organic Sol Food High-Potency Vitamin D3+K2
Good for: Those looking for a chewable vitamin D supplement made with organic, vegan ingredients
Featuring 5,000 IU of vitamin D3 naturally-sourced from lichen and 100 mcg of vitamin K2 from chickpeas, Ora Organic Sol Food High Potency Vitamin D3 + K2 is a once-daily chewable vitamin with a satisfaction guarantee. Users love the ease of use and the fresh citrus flavor.
What our tester says:
“The citrus flavor is nice and pleasant, not too sweet or powerful at all. These chewable tablets chew right up and dissolve in your mouth, too. I had no issues.”
Best Softgel Vitamin D Supplement: True Nutrition Vitamin D3
Good for: Active individuals looking for a vitamin D softgel that’s easy to swallow (price-wise too)
True Nutrition Vitamin D3 is a single-serving, potent vitamin D3 softgel, backed by third-party testing. It’s also budget-friendly and comes with 120 servings per bottle.
What our tester says:
“The softgels are small and very easy to swallow, especially since it’s just one at a time.”
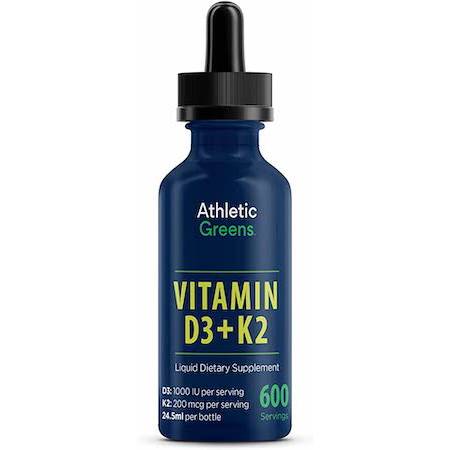
Best Liquid Vitamin D Supplement: Athletic Greens D3 + K2 Liquid
Good for: Vitamin D seekers who prefer a liquid, mixable option
If you are looking for an easy way to boost levels of vitamin D3 and K2, Athletic Greens’ Vitamin D3 + K2 liquid is a flavorless supplement that can easily be put in any beverage.
What our tester says:
“With the lack of sun in the winter I think supplementing with Vitamin D where I live plays a huge role in overall immune system health.”
Best Gummy Vitamin D Supplement: Bulletproof A+D+K Gummy
Good for: Kids at heart with adult vitamin D needs
The Bulletproof Vitamin A+D+K Gummies provide potent doses of each vitamin in one gummy. With no added sugars, these gummies can be a nice alternative for those who struggle swallowing pills.
What our tester says:
“These are SO GOOD. I’m almost out of these gummies and I’m really sad about it.”
Best Vitamin D and K Supplement: Thorne Vitamin D+K2 Drops
Good for: Vitamin D-rop searchers who prefer liquid over capsules and chewables
Thorne Vitamin D/K2 liquid supplement is a convenient and affordable way to increase your intake of both vitamin D3 and vitamin K2.
What our tester says:
“These drops are tasteless, and I love that you can mix it into a beverage. I find them easier than taking a pill everyday.”
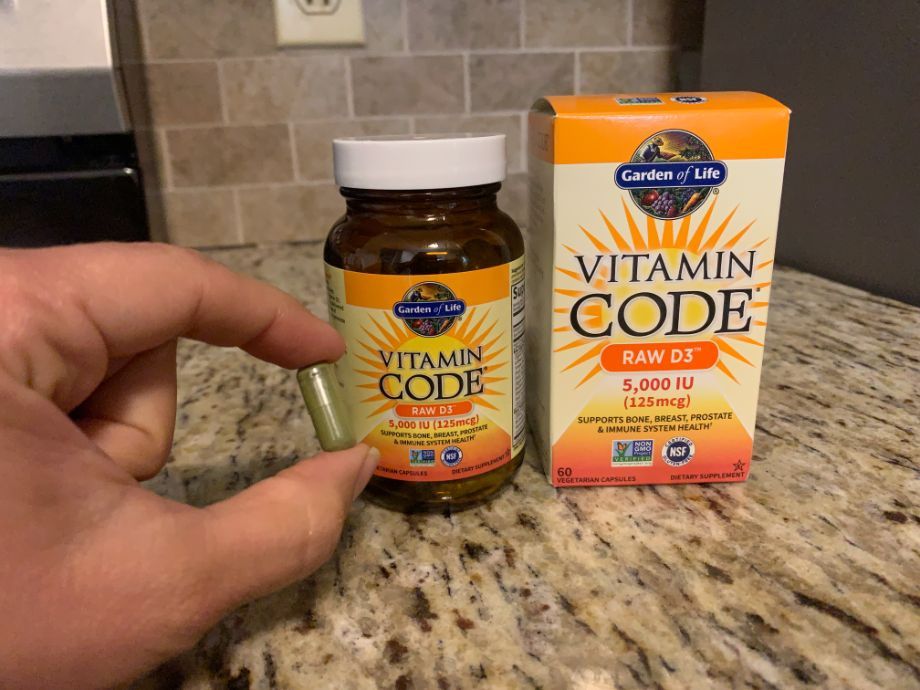
Best Organic Vitamin D Supplement: Garden of Life Vitamin Code Raw D3
Good for: Whole food advocates looking for a boost of vitamin D, probiotics, and nutrients
The Garden of Life Vitamin Code Raw D3 is a gluten- and dairy-free whole food vitamin D complex that also contains a healthy dose of probiotics and digestive enzymes.
What our tester says:
“These capsules do taste a bit plant-like when I have them, but it’s not off-putting by any means.”
Best Vitamin D Supplement for Kids: Carlson Labs Kid’s Super Daily Vitamin D3+K2
Good for: Kiddos recommended to an effective and high-quality vitamin D supplement
Made in an FDA-registered laboratory, Carlson’s Kid’s Super Daily Vitamin D3 + K2 liquid supplement provides 25 micrograms (1,000 international units) of concentrated vitamin D3 and 22.5 micrograms of vitamin K2 per serving.
What our tester says:
“After a bad reaction with a couple other brands for my second child, I switched to this brand after reading reviews and seeing they were vegetarian and gluten-free. It worked great! I’ll be using this for my third child too.”
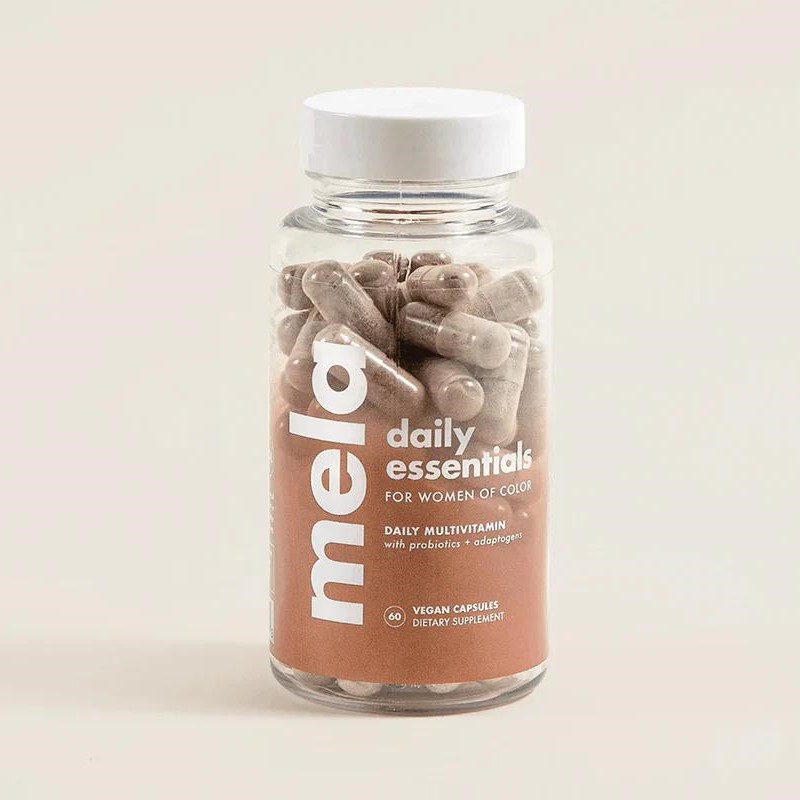
Best Vitamin D Supplement for Black Women: Mela Vitamins Daily Essentials for Women
Good for: Women with darker skin who are likely to have vitamin D deficiencies
Mela Vitamins Daily Essentials for Women is made by and for women of color. Specifically, the multivitamin contains high doses of vitamins D3 and B12 to help combat deficiencies and to support energy levels and healthy red blood cells, respectively. Additionally, this multivitamin has five strains of probiotics to help with gut health and digestion.
What our tester says:
“These multivitamins don’t taste very bad, so long as you don’t let them rest on your tongue for too long.”
Best Calcium and Vitamin D Supplement: Thorne Advanced Bone Support
Good for: People who want a supplement for bone health
Thorne Advanced Bone Support is formulated to help support bone health, particularly people who need extra support, like those diagnosed with osteoporosis. This supplement contains calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D, all used to help support bone health. Additionally, this multivitamin is gluten-free and free of major allergens.
What our tester says:
“I’ve used Thorne supplements throughout my athletic career because of their rigorous third-party testing. I always am confident that their supplements are free of contaminants and banned substances.”
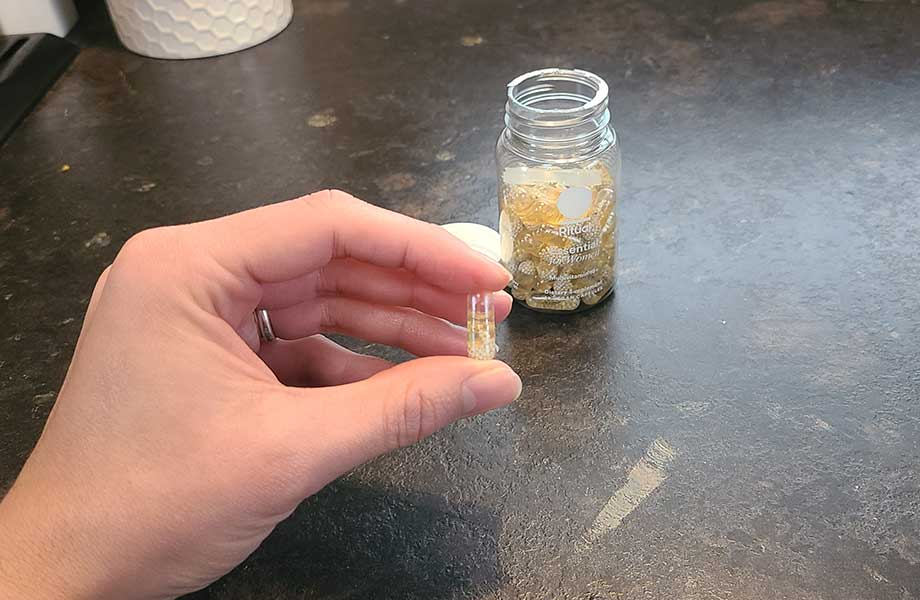
Best Vitamin D Supplement for Women: Ritual Essential for Women 18+
Good for: Women looking for a high-quality, effective dose of vitamin D
Ritual Essential for Women is a clinically-backed, vegan multivitamin made with nine high-quality traceable ingredients.
What our tester says:
“The minty flavor is quite pleasant; definitely preferable to a typical pill flavor! I also didn’t get any stomach issues that I typically do with other vitamin supplements.”
Other Vitamin D Supplements We Researched
Because there are hundreds of vitamin D supplements out, it’s nearly impossible to capture other great finds into one small, yet mighty list. Beyond our top picks, other vitamin D supplements we researched and approve include:
- Nordic Naturals Zero Sugar Vitamin D3 Gummies
- TheraCal D2000 Bone Health Supplement
- NATALIST Vitamin D3 Gummies
- Source Naturals Vitamin D-3 Liquid Drops
- Designs for Health Liposomal D Supreme Vitamin D
How We Picked and Tested the Best Vitamin D Supplements
We take our product reviews very seriously and the same goes for picking and testing the best vitamin D supplements on the market. To form our top picks, we specifically analyzed and factored in the following:
- Vitamin D type: As we’ve mentioned, vitamin D3 shows to be the most effective for increasing blood levels of vitamin D. This said, we are preferential towards vitamin D3 and each of our chosen products contains this form.
- Additional ingredients: If additional ingredients are formulated with vitamin D, what’s the intention? The inclusion of extra virgin olive oil is a great example of this, as the fat source can help enhance the absorption of the fat-soluble vitamin. We also favor products with cleaner formulas that are free of artificial ingredients, fillers, and other lower-quality, unnecessary ingredients.
- Supplemental form: Consumers differ on how they wish to take a supplement—such as a liquid or softgel—so we captured various supplemental forms to honor various preferences.
- Cost: While vitamin D supplements tend to be budget-friendly as a whole, we made sure to pick assorted price points to accommodate just about every personal budget.
- Manufacturing and testing: Because supplements are not tightly regulated, we always always prioritize products that have undergone tight manufacturing and testing practices. This includes compliance with the Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) set and monitored by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
- Brand loyalty: Is the company committed to high-quality products? Do they strive to keep customers both informed and satisfied? Just as we’re loyal to our review process and consumers, we place major weight on brands that do the same.
Benefits of Vitamin D Supplements
Some health benefits of vitamin D are familiar, but others are less obvious. Regardless, what vitamin D can do for the body and health is impressive and all backed by research.
Supports Bone Health
One of the most obvious and notable functions of vitamin D is its critical role to build and support healthy bones. Vitamin D deficiency also increases the risk of rickets in children, as well as osteomalacia and osteoporosis in adults.
This is because the body needs vitamin D20 for calcium absorption; and without enough of each, the body will start pulling available calcium in the skeletal system and eventually weaken bones. Supporting data21 clearly indicates that inadequate vitamin D over long periods of time can lead to bone demineralization.

A meta-analysis22 shows that vitamin D supplementation does not appear to improve bone health for those with adequate vitamin D levels. However, 2019 research23 advises that vitamin D intake of 800 IU per day—in tandem with sufficient calcium intake—is optimal for fracture prevention.
Protects from Several Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases24 are conditions that last one year or more—like heart disease, Type 2 diabetes, and cancer—and are the leading causes of death and disability in the U.S. Lifestyle factors, including diet and exercise, mainly contribute to the risk of chronic disease but vitamin D also shows to protect from the following:
- Heart/cardiovascular disease: A 2014 meta-analysis25 suggests vitamin D supplementation might protect against heart failure in older adults. A supporting 2019 systematic review and meta-analysis26 shows supplementing with vitamin D may reduce blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
- Cancer: Research27 proposes that low blood vitamin D is associated with an increased risk of 15 different cancers—including breast, colon, lung, and prostate cancers—whereas adequate vitamin D may reduce the growth and spread of malignant (cancer) cells. Another systematic review28 also found that vitamin D supplementation could reduce the risk of cancer death by 15%.
- Type 2 diabetes: Because vitamin D deficiency is linked to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, researchers continue examining if vitamin D supplementation could prevent or help manage the chronic disease. Although a 2017 review29 advises vitamin D supplementation cannot be recommended to prevent or improve Type 2 diabetes at this time, a recent 2022 study30 hints vitamin D could be effective in decreasing diabetes in adults with prediabetes.
Promotes Muscle Function and Recovery
Along with bone health, vitamin D can be integral in maintaining and supporting muscle strength and function. Recent research31 has even suggested that vitamin D can promote muscle regeneration after an injury, including fiber damage from resistance training. Likewise, muscular atrophy and defects have been reported with those with severe vitamin D deficiency, according to a 2018 review32. The same review showed an association between low vitamin D and an increase in falls or limb weakness.
While more research needs to be done to demonstrate the impact of vitamin D supplementation on athletic performance, it certainly will benefit athletes to maintain healthy levels of vitamin D to get the most out of their training, muscle-building, and reecovery.
Bolsters Immune Function
The immune system helps the body defend against harmful invaders, and 2011 data33 suggests lower levels of vitamin D may increase the risk of infections. Cells of the immune system—like B cells, T cells, and monocytes—may also positively respond to vitamin D, thus bolstering immune function, especially in individuals managing an autoimmune disease.
A more recent 2020 review published in Nutrients34 tells us that vitamin D shows to exert immunological activities on many immune system responses. There have also been associations between low levels of vitamin D and greater risks of immune-related health conditions, including psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Can Promote Digestive Health
While this is a growing field of study still, vitamin D has been associated with a healthy microbiome in the intestines, according to recent reviews35. A higher intake of vitamin D seems to have a positive impact in the probiotics in your gut, although studies have been a little mixed on how effective it is. More research should be done to determine the actual effects, but initial findings do seem promising.
Boosts Mental and Cognitive Health
Have you ever felt down in the dumps, only to get an instant mood and energy jolt after basking in the sweet sunshine? Well, not only can getting out in the sun boost your mood, but vitamin D supplementation might as well.

A 2020 systematic review and meta-analysis36, covering 25 trials and 7,500+ participants, found that vitamin D supplementation can reduce negative emotions. The benefits may be more pronounced in patients with major depressive disorders and individuals with vitamin D deficiency, though the evidence appears promising.
Furthermore, adequate vitamin D supplementation can the brain from inflammation and free radicals, which is linked37 to cognitive decline and degenerative disorders like dementia or Alzheimer’s disease. Healthy vitamin D levels can reduce your risk of these and other mental health disorders, too.
Supports Weight Loss
Fat loss is the byproduct of lifestyle factors, especially diet, and vitamin D might surprisingly play a role. Interestingly, obesity can increase the risk of vitamin D deficiency whereas weight loss can increase vitamin D levels according to a 2011 study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition38.
In a 2018 study39, researchers conducted a double-blind clinical trial on 50 overweight and obese women: one group received 50,000 IU of vitamin D per week while the other group received a placebo for six weeks. The group receiving vitamin D significantly reduced weight, waist circumference, and body mass index while increasing blood levels of vitamin D.
A less recent, yet larger 2014 study40 prescribed over 200 overweight and obese women (aged 50-75 years) with a calorie-restricted diet and exercise routine—and half of the women received 2,000 IU daily of vitamin D3, or and the other half took a placebo. After one year, the researchers found women who repleted vitamin D stores experienced greater improvements in their weight loss.
Sources of Vitamin D
There are different ways to get vitamin D; the most unique out of them (and easiest, depending on your location) is through natural sunlight. All you need to do is make sure your arms aren’t blocked by a long-sleeve shirt, and go out into direct sunlight in the middle of the day, and you’ll have your recommended amount of vitamin D in about 20 minutes.
Still, some locations might not get a lot of sunlight, and certain times of the year will also prove difficult to get direct sunlight. For those times, you may want to supplement vitamin D, or look to getting the nutrient in foods as well.
Vitamin D shows up in certain foods, and other foods can also be fortified with vitamin D. Here are common sources of vitamin D in foods we eat:
- Egg yolks
- Fatty fish like salmon or tuna
- Cheese
- Liver
- Fortified foods like milk, cereal, or orange juice
Vitamin D supplements are also a viable option, and might especially be needed if you’re deficient in the vitamin.
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
There are many symptoms of vitamin D deficiency, but not everyone experiences all (or any) of these symptoms. If you suspect you are deficient in vitamin D, or another micronutrient, consult with your physician on the best course of action. Common symptoms can include41:
- Muscle and/or bone pain
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue
- Depression
- Brittle bones
Because of vitamin D’s role in bone health, in extreme cases, bones may become deformed or a person may develop bowed legs.
Dosing and Interactions
While vitamin D supplements are mostly considered to be safe, you should still dose accordingly. Vitamin D can also interact with certain medications, which could pose serious risks and/or reduce the efficacy of the supplement or prescription.
Dose Recommendations
The amount of vitamin D you need each day is based on Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs), or the average daily intake level to meet nutrient requirements. Provided by the National Institutes of Health7, the RDAs below indicate daily intakes sufficient to maintain bone health and calcium metabolism in healthy metabolism:
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy & Lactation |
| 0-12 months* | 10 mcg (400 IU) | 10 mcg (400 IU) | |
| 1-13 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | |
| 14-18 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
| 19-50 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) |
| 51-70 years | 15 mcg (600 IU) | 15 mcg (600 IU) | |
| >70 years | 20 mcg (800 IU) | 20 mcg (800 IU) |
*Recommendation based on Adequate Intake (AI)
Interestingly, too, a 2020 review27 hints there’s still debate on what level of vitamin D in the blood is optimal to achieve the health benefits of vitamin D. However, it’s likewise advisable to increase vitamin D intake—and have sensible sunlight exposure—to maintain levels.
To add more complexity to the matter, vitamin D testing can be expensive and not always supported as a screening tool2. For successful repletion of vitamin D, it’s prudent to mention who might be at the greatest risk of deficiency which includes:
- People who cannot tolerate or avoid dairy products or follow a vegan diet
- Those who are classified as obese
- Individuals condition that impacts the digestive system, including Crohn’s disease and conditions that interfere with normal fat digestion
- People who have undergone gastric bypass surgery
- Darker-skinned individuals or those who are regularly fully-clothed/use sunscreen that blocks vitamin D absorption from the sun
- Older adults, especially who spend more time indoors
- Those who live in the northern hemisphere, especially when winter arrives and sun exposure lessens
All this said, recommended intake values also vary based on an individual’s vitamin D level. Someone with a significant vitamin D deficiency will require more vitamin D to replete those vitamin D stores.
Interactions & Safety
It’s smart to consult with your doctor before taking any sort of supplement, especially if you’re taking medication. This is because there’s always a risk of drug interactions, which can make the prescription less effective and/or lead to unwanted—and sometimes dangerous and fatal—side effects.
Mayo Clinic42 counsels the following medications can lead to possible interactions, including:
- Aluminum
- Anticonvulsants, specifically phenobarbital and phenytoin
- Atorvastatin
- Calcipotriene
- Cholestyramine
- Cytochrome P-450 3A4 substrates
- Digoxin
- Diltiazem
- Orlistat
- Thiazide diuretics
- Steroids
- Stimulant laxatives
- Verapamil
Beyond medication interactions, vitamin D supplementation shows to be safe and toxicity is rare13. Severe adverse effects have only been reported with very extreme intakes of vitamin D ranging from 15,000-42,000 mcg, which is well above natural intakes from food or supplements.
Still, most of the risks are related to vitamin D’s function of increasing calcium absorption—the more vitamin D available, the more calcium that’s absorbed, which can cause hypercalcemia. Defined as high calcium in the blood, hypercalcemia43 can cause bone pain, digestive complications, kidney stones and failure, depression, and other worrisome health concerns.
It might sound like a broken record, but it’s genuinely important to seek medical guidance to help determine your unique nutrient needs.
Buying Guide: What to Look for in Vitamin D Supplements
Whether you’re looking for additional guidance to choose between our top picks or venturing outside the list, lean on these expert tips to decide which vitamin D supplement is right for you.

Review the Formulation
The formulation is what you’ll actually be consuming, so it’s important to review it. Here’s what to look out for in a vitamin D supplement:
- Vitamin D form: Vitamin D supplements mostly contain one of two forms, including vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) or vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). Both are great sources of vitamin D but we do recommend choosing a supplement with vitamin D3 since it’s more effective in raising vitamin D levels in the blood.
- Vitamin D content: Most vitamin D supplements provide 1,000-2,000 IUs of vitamin D, although some offer higher doses. Ultimately, you and your doctor should explore together how much vitamin D might be best for your individual needs and select a dosage to match.
- Added ingredients: Beyond vitamin D, review and consider additional ingredients in the supplement. For instance, some vitamin D supplements contain other nutrients such as vitamins A and K while others (outside of our picks) might contain unwanted fillers.
Consider the Supplement Form
Would you rather consume the vitamin D supplement as liquid drops, softgels, or gummies? Pick a supplement form based on your preferences, as you’ll be more consistent in taking it if it’s in a preferential form.
Factor in Your Dietary Needs and Preferences
Do you follow a vegan diet? Or perhaps you’re managing Celiac disease and needing a gluten-free option. Consider your dietary needs and/or preferences and choose a vitamin D supplement to match.
Explore Verifications and Certifications
Exploring the product verification and certifications can give you great insight into what’s actually in the supplement. (And what’s not in the product.)
Look out for third-party testing verifications to best validate the product’s safety, purity, and quality. Also, check to see if the product holds verifications that are important to you like certified gluten-free and/or vegan.
Investigate the Brand Behind the Product
Investigating the brand behind the product of interest can deepen your understanding of the brand’s standards and reputation. Areas that can provide great insight include:
- Return policies and 100% money-back guarantees
- Customer reviews on the site’s main webpage, as well as on Amazon and other third-party seller sites if available
- Customer service access or at minimum a contact form you can fill out—and actually get a response back
Taking this extra step can help you decide if you’re willing to support a company (and acquire your hard-earned dollars)!
FAQs About Vitamin D Supplements
Which form of vitamin D is best absorbed?
Research suggests vitamin D3 is the best form to take rather than vitamin D2. Both forms act and function similarly in the body, although vitamin D3 shows to be effective in increasing vitamin D levels.
How much vitamin D should you take every day?
How much vitamin D you should take depends on many factors, including your age and current vitamin D status. As a general rule, most males and females should consume 15 mcg (600 IU) of vitamin D daily and increase to 20 mcg (800 IU) after age 70.
Is it better to take vitamin D in the morning or at night?
When it comes to timing your vitamin D supplements, all that matters is to follow the dosing instructions. Some supplements require you take with a meal or a certain amount of water.
What is the difference between Vitamin D and Vitamin D3?
Vitamin D3, also known as cholecalciferol, is a form of vitamin D. Vitamin D is available in different forms, primarily D2 and D3. The two forms of vitamin D2 and D3 are both produced through sunlight exposure, making them very similar at a glance.
However, vitamin D3 is mostly discussed in vitamin D supplements because this form seems to be more potent and effective in the body than D2, although the studies with these findings are older4.
References
- Amrein K, Scherkl M, Hoffmann M, et al. Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2020 Nov;74(11):1498-1513. doi: 10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y. Epub 2020 Jan 20. PMID: 31959942; PMCID: PMC7091696.
- Kennel KA, Drake MT, Hurley DL. Vitamin D deficiency in adults: when to test and how to treat. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010;85(8):752-758. doi:10.4065/mcp.2010.0138
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. (2024, May 9). Vitamin D. The Nutrition Source. https://nutritionsource.hsph.harvard.edu/vitamin-d/
- Armas LA, Hollis BW, Heaney RP. Vitamin D2 is much less effective than vitamin D3 in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Nov;89(11):5387-91. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-0360. PMID: 15531486.
- Halder M, Petsophonsakul P, Akbulut AC, et al. Vitamin K: Double Bonds beyond Coagulation Insights into Differences between Vitamin K1 and K2 in Health and Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(4):896. Published 2019 Feb 19. doi:10.3390/ijms20040896
- Vieth R. Vitamin D Toxicity, Policy, and Science. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(S2):V64-V68. doi:https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.07s221
- National Institutes of Health. (Updated July 26, 2024). Office of Dietary Supplements – Vitamin D. Nih.gov. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/
- Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Jul;96(7):1911-30. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-0385. Epub 2011 Jun 6. Erratum in: J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Dec;96(12):3908. PMID: 21646368.
- Hirsch, L. Arnold. Industrial Aspects of Vitamin D. Academic Press. 2011. doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-381978-9.10006-X.
- USDA. (n.d.). U.S. Forest Service. Forest Service Shield. https://www.fs.usda.gov/wildflowers/beauty/lichens/about.shtml
- Hogarth, C. A., & Griswold, M. D. (2010). The key role of vitamin A in spermatogenesis. The Journal of clinical investigation, 120(4), 956–962. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI41303
- van Ballegooijen AJ, Pilz S, Tomaschitz A, Grübler MR, Verheyen N. The Synergistic Interplay between Vitamins D and K for Bone and Cardiovascular Health: A Narrative Review. Int J Endocrinol. 2017;2017:7454376. doi: 10.1155/2017/7454376. Epub 2017 Sep 12. PMID: 29138634; PMCID: PMC5613455.
- National Institutes of Health. (Updated August 12, 2022). Office of Dietary Supplements – Vitamin A. Nih.gov. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminA-Consumer/
- Kozioł-Kozakowska A, Maresz K. The Impact of Vitamin K2 (Menaquionones) in Children’s Health and Diseases: A Review of the Literature. Children (Basel). 2022;9(1):78. Published 2022 Jan 5. doi:10.3390/children9010078
- Fu X, Harshman SG, Shen X, et al. Multiple Vitamin K Forms Exist in Dairy Foods. Curr Dev Nutr. 2017 Jun 1;1(6):e000638. doi: 10.3945/cdn.117.000638. PMID: 29955705; PMCID: PMC5998353.
- Young, A. R., Morgan, K. A., Ho, T. W., Ojimba, N., Harrison, G. I., Lawrence, K. P., Jakharia-Shah, N., Wulf, H. C., Cruickshank, J. K., & Philipsen, P. A. (2020). Melanin has a Small Inhibitory Effect on Cutaneous Vitamin D Synthesis: A Comparison of Extreme Phenotypes. The Journal of investigative dermatology, 140(7), 1418–1426.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2019.11.019
- National Institutes of Health (2024). Vitamin B12 – Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. NIH Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-HealthProfessional/
- Joshi, M., Hiremath, P., John, J., Ranadive, N., Nandakumar, K., & Mudgal, J. (2023). Modulatory role of vitamins A, B3, C, D, and E on skin health, immunity, microbiome, and diseases. Pharmacological reports : PR, 75(5), 1096–1114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-023-00520-1
- Voulgaridou, G., Papadopoulou, S. K., Detopoulou, P., Tsoumana, D., Giaginis, C., Kondyli, F. S., Lymperaki, E., & Pritsa, A. (2023). Vitamin D and Calcium in Osteoporosis, and the Role of Bone Turnover Markers: A Narrative Review of Recent Data from RCTs. Diseases (Basel, Switzerland), 11(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11010029
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2023, July 13). Bone Health and osteoporosis. National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/bone-health-and-osteoporosis
- Laird E, Ward M, McSorley E, et al. Vitamin D and bone health: potential mechanisms. Nutrients. 2010;2(7):693-724. doi:10.3390/nu2070693
- Bolland MJ, Grey A, Avenell A. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on musculoskeletal health: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6(11):847-858. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(18)30265-1
- Yao P, Bennett D, Mafham M, et al. Vitamin D and Calcium for the Prevention of Fracture: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(12):e1917789. doi:https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.17789
- CDC. (2024, October 04). About chronic diseases. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed October 17, 2024 from: https://www.cdc.gov/chronic-disease/about/index.html
- Ford JA, MacLennan GS, Avenell A, et al. Cardiovascular disease and vitamin D supplementation: trial analysis, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;100(3):746-755. doi:https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.113.082602
- Dibaba DT. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on serum lipid profiles: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Rev. 2019;77(12). doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuz037
- Holick MF. Cancer, sunlight and vitamin D. J Clin Transl. Endocrinol 2014;1(4):179-186. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcte.2014.10.001
- Zhang Y, Fang F, Tang J, et al. Association between vitamin D supplementation and mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. Published online August 12, 2019:l4673. doi:https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4673
- Lips P, Eekhoff M, van Schoor N, et al. Vitamin D and type 2 diabetes. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Oct;173:280-285. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.11.021. Epub 2016 Dec 5. PMID: 27932304.
- Pittas AG, Kawahara T, Jorde R, et al. Vitamin D and Risk for Type 2 Diabetes in People With Prediabetes. Ann Intern Med. Published online February 7, 2023. doi:https://doi.org/10.7326/m22-3018
- Latham CM, Brightwell CR, Keeble AR, Munson BD, Thomas NT, Zagzoog AM, Fry CS and Fry JL (2021) Vitamin D Promotes Skeletal Muscle Regeneration and Mitochondrial Health. Front. Physiol. 12:660498. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.660498
- Gunton, J. E., & Girgis, C. M. (2018). Vitamin D and muscle. Bone reports, 8, 163–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bonr.2018.04.004
- Aranow C. Vitamin D and the immune system. J Investig Med. 2011;59(6):881-886. doi:10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755
- Charoenngam N, Holick MF. Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease. Nutrients. 2020 Jul 15;12(7):2097. doi: 10.3390/nu12072097. PMID: 32679784; PMCID: PMC7400911.
- Bellerba, F., Muzio, V., Gnagnarella, P., Facciotti, F., Chiocca, S., Bossi, P., Cortinovis, D., Chiaradonna, F., Serrano, D., Raimondi, S., Zerbato, B., Palorini, R., Canova, S., Gaeta, A., & Gandini, S. (2021). The Association between Vitamin D and Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review of Human Studies. Nutrients, 13(10), 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103378
- Cheng Y, Huang Y, Huang W. The effect of vitamin D supplement on negative emotions: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Depress Anxiety. Published online May 4, 2020. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/da.23025
- Anjum, I., Jaffery, S. S., Fayyaz, M., Samoo, Z., & Anjum, S. (2018). The Role of Vitamin D in Brain Health: A Mini Literature Review. Cureus, 10(7), e2960. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.2960
- Mason C, Xiao L, Imayama I, et al. Effects of weight loss on serum vitamin D in postmenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;94(1):95-103. doi:10.3945/ajcn.111.015552
- Khosravi ZS, Kafeshani M, Tavasoli P, et al. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Weight Loss, Glycemic Indices, and Lipid Profile in Obese and Overweight Women: A Clinical Trial Study. Int J Prev Med. 2018;9:63. Published 2018 Jul 20. doi:10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_329_15
- Mason C, Xiao L, Imayama I, et al. Vitamin D3 supplementation during weight loss: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014 May;99(5):1015-25. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.113.073734. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Erratum in: Am J Clin Nutr. 2014 Oct;100(4):1213. PMID: 24622804; PMCID: PMC3985208.
- National Institutes of Health (2023). Vitamin D – Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. NIH Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/
- Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2023, August 10). Vitamin D. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-vitamin-d/art-20363792
- Sadiq NM, Anastasopoulou C, Patel G, et al. Hypercalcemia. [Updated 2024 May 7]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430714/